
The Sun
The Sun is the center of our solar system, around which all planets orbit. Like all stars, the Sun’s a giant ball of super heated hydrogen gas. Comprising 98.6 percent of the solar system’s total mass, the Sun provides nearly all of the Earth’s energy as electromagnetic radiation. The absorption, reflection and redistribution of this energy from the Sun shapes the weather and climate of our planet. The Sun’s surface is not firm like the Earth’s; but is composed of churning active gases, hot enough to vaporize any solid. The energy produced and emitted by the Sun provides warmth and light for all planets. Containing only seven percent of the Sun’s volume, but half its mass, the inner core fuels the star with nuclear fusion.
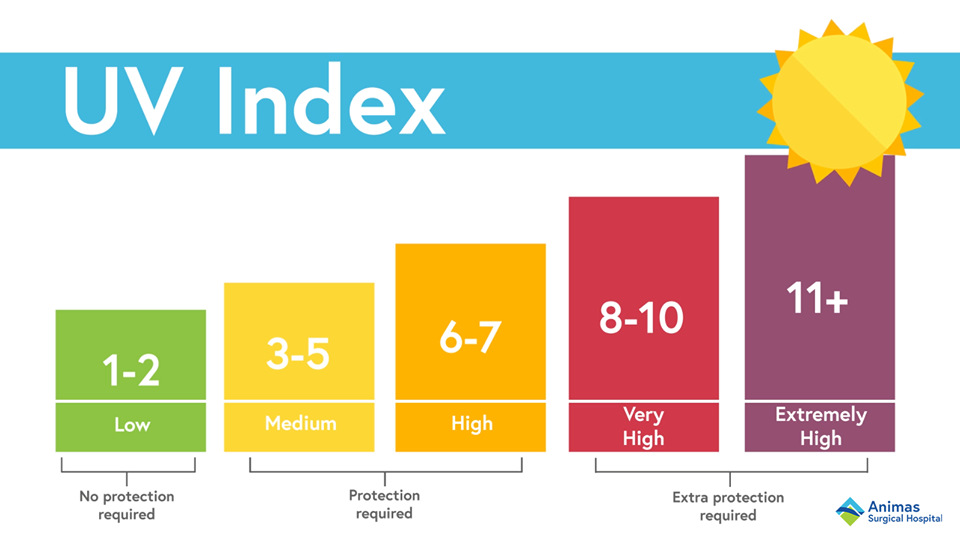
UV Index
This index is an international standard measurement of the strength of Ultraviolet (UV) radiation at a particular place and time. The purpose of the UV Index is to help people effectively protect themselves from UV radiation, which has health benefits in moderation but in excess causes sunburn, skin aging, DNA damage, skin cancer, eye damage such as cataracts and immunosuppression.
Some Negative Impacts
Most are familiar with the harmful effects associated with exposure to direct sunlight. Like many things in life, too much sun may be detrimental to one’s health.
- Long-term, unprotected exposure to direct sunlight can damage the retina. This may cause blurred vision and possibly cataracts in the long run.
- Too much sunshine can cause excessive sweating. Sweating leads to the loss of water and essential salts in the body. This may result in heat exhaustion. If heat exhaustion is left untreated, it can lead to heat stroke. Heat stroke is the most serious heat-related illness and can be life-threatening. Heat stroke causes the temperature of the body to rise quickly.
- Sunburns are widely recognised as one of the most common negative effects of too much sun exposure. The symptoms of sunburn do not usually appear until about four or five hours after the sun exposure occurs.
- The worst consequence of long-term exposure to the sun is the development of skin cancer. Because the sun damage to the skin develops over years, the older you are, the greater the risk of developing skin cancer. After years of exposure to the sunlight, specialists look for three common types of skin cancer.
- Sun exposure is a significant factor in the development of wrinkles. UV radiation damages collagen and elastic tissue in the skin, so it becomes fragile and does not spring back into shape, causing sagging. UV light exposure also causes white and dark spots on the skin, as it damages the surface cells.
Some Positive Impacts
Very often, the Sun has the reputation for only leaving a negative impact on our health, when in fact, its benefits are many. Like many things in life, sunshine should be enjoyed in moderation.
- It enhances your mood. Being in the Sun can help people feel better and more energetic. Sunlight increases the levels of serotonin in the brain. Serotonin is associated with improved mood. Not surprisingly, serotonin levels are highest in the summer months.
- It helps relieve stress. Life in itself induces stress. Be it through work, family or health related issues. Stress can be relieved in various ways. One of them is through exposure to sunlight.
- It helps treat Seasonal Affective Disorder. In some people, the lack of sunlight in winter can trigger depression. Symptoms include bad moods, difficulty making and keeping friends, overeating, tiredness and sleeping far too much.
- It improves sleep quality. Exposure to sunlight impacts how much melotonin your body produces. Melotonin is the chemical that tells your brain when it is time to sleep. With a lack of sunlight, your body produces far more melotonin than is needed. Hence, you feel tired and ready to sleep more often and earlier.
- It provides you with Vitamin D. It is often referred to as the sun vitamin. Vitamin D is involved in maintaining a healthy body. One way you can get this vitamin is exposure to the ultraviolet light from the sun.
You don’t need much time in the sun to take advantage of these benefits. Only 15 to 30 minutes of sun exposure is all you need.


0 comments
Write a comment